Azure Data Factory: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know
Unlock the full potential of cloud data integration with Azure Data Factory—a game-changing service that simplifies how you build, manage, and scale data pipelines in the cloud. Whether you’re a data engineer or a cloud architect, this guide breaks down everything you need to know.
What Is Azure Data Factory?

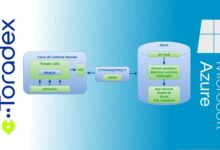
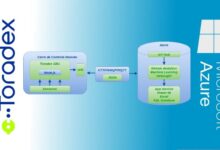
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is Microsoft’s cloud-based data integration service that enables organizations to create data-driven workflows for orchestrating and automating data movement and transformation. It allows you to ingest data from diverse sources, transform it using various compute services, and deliver it to destinations for analytics and reporting.
Core Purpose and Use Cases
At its heart, Azure Data Factory is designed to solve complex data integration challenges in hybrid and cloud environments. It’s commonly used for Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) and Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) processes, enabling businesses to consolidate data from on-premises databases, SaaS applications, and cloud storage into centralized data warehouses or lakes.
- Automating nightly data syncs from CRM systems like Salesforce.
- Building real-time data pipelines for IoT telemetry ingestion.
- Orchestrating machine learning workflows by chaining data preparation and model training jobs.
How It Fits Into the Azure Ecosystem
Azure Data Factory doesn’t work in isolation. It integrates seamlessly with other Azure services such as Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Databricks, Azure Blob Storage, and Azure SQL Database. This tight integration allows for end-to-end data solutions without the need for custom glue code.
For example, ADF can trigger an Azure Databricks notebook to clean and enrich data, then load the results into Azure Synapse for enterprise reporting. The service also supports integration with HDInsight, Azure Functions, and Logic Apps, making it a central orchestrator in modern data architectures.
“Azure Data Factory is the backbone of our enterprise data platform. It enables us to automate 90% of our data workflows with minimal operational overhead.” — Cloud Architect, Fortune 500 Company
Key Components of Azure Data Factory
To understand how Azure Data Factory works, it’s essential to grasp its core components. These building blocks form the foundation of every data pipeline you create.
Pipelines and Activities
A pipeline in Azure Data Factory is a logical grouping of activities that perform a specific task. For instance, a pipeline might include activities to copy data from an on-premises SQL Server to Azure Blob Storage, followed by a transformation using Azure Databricks.
Activities are the atomic units of work and fall into three main categories:
- Data movement activities: Copy data between sources and sinks.
- Data transformation activities: Execute transformations using services like Databricks, HDInsight, or Azure Functions.
- Control activities: Manage pipeline flow with constructs like If Condition, ForEach, and Execute Pipeline.
Linked Services and Datasets
Linked services define the connection information needed to connect to external resources. Think of them as connection strings that hold credentials and endpoint details. You can create linked services for Azure SQL Database, Amazon S3, or even on-premises SQL Server via the Self-Hosted Integration Runtime.
Datasets, on the other hand, represent the structure and location of data within a data store. A dataset might point to a specific table in a database or a folder in blob storage. They are used as inputs and outputs in activities.
Integration Runtimes
The Integration Runtime (IR) is the compute infrastructure that Azure Data Factory uses to achieve data integration across different network environments. There are three types:
- Azure Integration Runtime: Used for public cloud data movement and transformation.
- Self-Hosted Integration Runtime: Enables data transfer between cloud and on-premises systems.
- Managed Virtual Network Integration Runtime: Used for secure, private data processing within a virtual network.
Choosing the right IR is critical for performance and security, especially when dealing with sensitive or regulated data.
Why Choose Azure Data Factory Over Alternatives?
With several data integration tools available—like AWS Glue, Google Cloud Dataflow, and Apache Airflow—why should you consider Azure Data Factory? The answer lies in its scalability, ease of use, and deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem.
Serverless Architecture and Scalability
Azure Data Factory is a fully managed, serverless service. This means you don’t have to provision or manage any infrastructure. The platform automatically scales based on the workload, handling everything from small batch jobs to massive data migrations.
For example, if you schedule a pipeline to run every hour and the data volume suddenly spikes, ADF dynamically allocates more resources to process the load without any manual intervention.
Visual Development Experience
One of the standout features of Azure Data Factory is its drag-and-drop visual interface. The pipeline designer allows users to build complex workflows without writing a single line of code. You can visually connect sources, transformations, and sinks using intuitive UI elements.
This low-code approach accelerates development and makes ADF accessible to both technical and non-technical users. Data analysts can build simple ETL flows, while engineers can extend them with custom code when needed.
Native Support for Hybrid Data Scenarios
Many enterprises still rely on on-premises databases and legacy systems. Azure Data Factory excels in hybrid scenarios thanks to the Self-Hosted Integration Runtime. This component acts as a bridge between your local network and the cloud, enabling secure data transfer without exposing internal systems to the public internet.
Unlike some competitors that require complex networking setups, ADF simplifies hybrid connectivity with minimal configuration.
Building Your First Azure Data Factory Pipeline
Creating a pipeline in Azure Data Factory is straightforward, even for beginners. Let’s walk through a practical example: copying data from an Azure Blob Storage container to an Azure SQL Database.
Step 1: Create a Data Factory Instance
Log in to the Azure Portal, navigate to the “Create a resource” section, and search for “Data Factory.” Select the service, choose your subscription and resource group, and give your factory a unique name. Once deployed, open the ADF studio to begin designing.
Step 2: Set Up Linked Services
In the ADF studio, go to the “Manage” tab and create two linked services:
- One for your Azure Blob Storage account (using the storage account key).
- Another for your Azure SQL Database (providing server name, database name, and authentication details).
These connections will be reused across multiple pipelines, promoting consistency and reducing configuration errors.
Step 3: Define Datasets and Build the Pipeline
Next, define datasets for the source (Blob Storage) and sink (SQL Database). Specify the container, folder path, and file format for the source, and the table name for the destination.
Then, create a new pipeline and drag a “Copy Data” activity onto the canvas. Configure it to use the source and sink datasets. You can also add pre- and post-copy scripts, such as truncating the destination table before loading.
Step 4: Test and Schedule the Pipeline
Use the “Debug” button to run the pipeline and verify that data flows correctly. Once successful, create a trigger to run the pipeline on a schedule—say, every day at 2 AM. ADF supports both time-based and event-based triggers, giving you flexibility in automation.
Advanced Capabilities of Azure Data Factory
Beyond basic data movement, Azure Data Factory offers powerful features for complex data workflows. These capabilities make it suitable for enterprise-grade data integration.
Data Flow: Code-Free Data Transformation
Azure Data Factory’s Mapping Data Flows feature allows you to perform transformations without writing code. It uses a Spark-based engine under the hood, providing scalability and performance.
You can perform operations like filtering rows, joining datasets, aggregating values, and deriving new columns using a visual interface. Data Flows automatically generate Spark code, which runs on a serverless Spark cluster managed by Azure.
For example, you can cleanse customer data by standardizing address formats, removing duplicates, and enriching it with geolocation data—all through a drag-and-drop interface.
Control Flow and Pipeline Orchestration
ADF supports advanced control logic within pipelines. You can use activities like If Condition, Switch, ForEach, and Until to create dynamic workflows.
Imagine a scenario where you need to process multiple files in a folder. You can use a ForEach activity to iterate over the file list, and within each iteration, apply a transformation and load the data. You can also chain multiple pipelines together using the Execute Pipeline activity for modular design.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Tools
Azure Data Factory provides robust monitoring through the Monitor hub in ADF Studio. You can view pipeline runs, check execution duration, and inspect input/output details for each activity.
If a pipeline fails, you can drill down into the error message, view logs, and even rerun failed activities individually. Integration with Azure Monitor and Log Analytics allows for centralized logging and alerting, helping teams respond quickly to issues.
Security and Compliance in Azure Data Factory
Security is a top priority when handling enterprise data. Azure Data Factory provides multiple layers of protection to ensure data integrity and compliance.
Authentication and Access Control
ADF supports Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) authentication and role-based access control (RBAC). You can assign roles like Data Factory Contributor, Reader, or custom roles to control who can create, edit, or view pipelines.
For linked services, you can use Azure Key Vault to securely store credentials like database passwords and API keys. ADF retrieves these secrets at runtime, minimizing the risk of exposure.
Data Encryption and Network Security
All data in transit is encrypted using TLS/SSL. For data at rest, ADF relies on the encryption capabilities of the underlying storage services (e.g., Azure Blob Storage uses AES-256 encryption).
To enhance network security, you can deploy ADF within a Virtual Network (VNet) using Managed Virtual Network and Private Endpoints. This ensures that data doesn’t traverse the public internet when moving between Azure services.
Compliance and Auditing
Azure Data Factory complies with major regulatory standards, including GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001, and SOC 2. Audit logs are available through Azure Monitor, capturing user actions, pipeline executions, and system events.
These logs can be exported to a Log Analytics workspace or Azure Storage for long-term retention and compliance reporting.
Best Practices for Optimizing Azure Data Factory
To get the most out of Azure Data Factory, follow these proven best practices for performance, maintainability, and cost efficiency.
Design Modular and Reusable Pipelines
Break down complex workflows into smaller, reusable pipelines. Use parameters and variables to make them dynamic. For example, create a generic “Copy Data” pipeline that accepts source and destination as parameters, then call it from multiple parent pipelines.
This approach reduces duplication, simplifies testing, and makes updates easier.
Optimize Data Flow Performance
When using Mapping Data Flows, choose the appropriate integration runtime and cluster size. For large datasets, increase the number of worker nodes or use a larger node type.
Also, optimize your data schema by selecting only the columns you need and using efficient file formats like Parquet or ORC instead of CSV.
Implement Robust Error Handling
Use Try-Catch patterns with the Execute Pipeline and Web Activity to handle failures gracefully. Send notifications via email or Teams using webhooks when a pipeline fails.
Log errors to a centralized store for analysis and root cause identification.
Monitor Costs and Usage
Azure Data Factory pricing is based on activity runs, data movement, and data flow execution time. Monitor your usage in the Azure Cost Management dashboard to avoid unexpected charges.
For example, a frequently triggered pipeline that processes small amounts of data might be more cost-effective using a tumbling window trigger with batching.
Real-World Use Cases of Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory is used across industries to solve real business problems. Here are a few compelling examples.
Retail: Unified Customer Analytics
A global retailer uses ADF to combine online sales data from Azure Cosmos DB, in-store transactions from on-premises SQL Server, and customer service logs from Dynamics 365. The unified dataset is loaded into Azure Synapse for 360-degree customer analysis, enabling personalized marketing campaigns.
Healthcare: Secure Patient Data Integration
A hospital network leverages ADF with Self-Hosted IR to extract anonymized patient records from legacy systems. The data is transformed in Azure Databricks and loaded into a HIPAA-compliant data lake for research and operational reporting.
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance
An industrial manufacturer uses ADF to ingest sensor data from IoT devices into Azure Event Hubs. Pipelines process the data in near real-time, feeding it into machine learning models hosted on Azure ML. Predictive alerts are generated when equipment shows signs of failure.
What is Azure Data Factory used for?
Azure Data Factory is used for orchestrating and automating data movement and transformation workflows in the cloud. It’s ideal for ETL/ELT processes, data migration, hybrid data integration, and building data pipelines for analytics and machine learning.
Is Azure Data Factory serverless?
Yes, Azure Data Factory is a fully managed, serverless service. You don’t need to manage infrastructure; the platform automatically scales resources based on workload demands.
How much does Azure Data Factory cost?
Pricing is based on activity runs, data movement, and data flow execution. The first 5,000 data movement activities per month are free. Detailed pricing can be found on the official Azure pricing page.
Can Azure Data Factory connect to on-premises databases?
Yes, using the Self-Hosted Integration Runtime, Azure Data Factory can securely connect to on-premises data sources like SQL Server, Oracle, and file shares.
How does Azure Data Factory compare to SSIS?
Azure Data Factory is the cloud evolution of SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS). While SSIS is designed for on-premises ETL, ADF offers cloud-native scalability, hybrid connectivity, and modern orchestration features. ADF also supports SSIS package migration via the Azure-SSIS Integration Runtime.
Azure Data Factory is a powerful, flexible, and secure platform for modern data integration. Whether you’re migrating legacy ETL systems, building real-time data pipelines, or orchestrating complex analytics workflows, ADF provides the tools and scalability to succeed. With its visual interface, serverless architecture, and deep Azure integration, it’s no wonder that organizations worldwide rely on Azure Data Factory to power their data-driven decisions. By following best practices and leveraging its advanced features, you can unlock the true potential of your data ecosystem.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: